Setup¶
There are two ways to setup this project. The easiest and cleanest is to use a Docker container. However, if you need the interaction to run upon bootup, you are probably better off setting up this project on your local machine (not in a Docker container). Below are instructions for both of these methods.
Using the Docker Container¶
- To run a Docker container, go into the
dockerdirectory in this project’s repository and run therunscript. Note that you can pass in various arguments to the run script: ./run.sh runwill start the vision project’s interaction./run.sh terminalwill give you access to a terminal inside the Docker container. Note, if you want additional terminals you candocker execinto the running container.- This is probably the best option if you are accessing QT remotely or using a non Linux operating system, as graphics won’t work.
./run.sh popupcreates a new terminal window from which you can launch other programs, such as PyCharm or RViz.
Note
If you have make installed, you can test that your Docker image is setup correctly and that you have valid Amazon Web Services (AWS) credentials by running make test_docker. Be aware that this script assumes that you have the following environmental variables set: AWS_SECRET_KEY_ID and AWS_SECRET_KEY. If you don’t have these set, add the following lines to the end of your ~/.bashrc and then source your ~/.bashrc: source ~/.bashrc.
export AWS_SECRET_KEY_ID="<my secret key id>"
export AWS_SECRET_KEY="<my secret key>"
In Your Current Environment¶
To run the interaction on your local machine, you’ll need to install several packages. If you have make installed (sudo apt update; sudo apt install -y make, on Ubuntu 16.04), you install the necessary dependencies with make install_deps. If you don’t have make installed, you can also access the script with ./docker/scripts/install_deps.sh.
Once you have the dependencies installed, you’ll need to clone several repositories into the src folder in your catkin workspace
git clone https://github.com/robotpt/vision-project.git
git clone https://github.com/robotpt/cordial.git
git clone https://github.com/robotpt/qt-robot.git
git clone https://github.com/robotpt/ros-data-capture.git
git clone https://github.com/RobotWebTools/rosbridge_suite.git
Finally, you will have to build your catkin workspace with catkin_make from the top folder of your catkin workspace. Note, make sure that you have your ROS environment sourced. After you make your workspace, you can run the tests to confirm that your environment is setup. Make sure you have run aws configure or setup your AWS configuration and credentials files manually.
source /root/catkin_ws/devel/setup.bash && rostest cordial_gui test_cordial_gui_actions.test && rostest cordial_gui test_cordial_gui_pubs_and_subs.test && rostest cordial_manager test_cordial_manager_actions.test && rostest cordial_manager test_cordial_manager_pubs_and_subs.test && rostest cordial_manager test_cordial_manager_services.test
Running the interaction remotely¶
Create a Dataplicity account and sign on. Go to the devices tab and then click “+ Add New Device”. Copy or enter this command into a terminal on QT’s body PC and enter QT’s password ‘qtrobot’. After that runs, remote access should be setup. You can confirm this by clicking the added device and confirming that you can explore the file system.
To run the vision project interaction, first run su qtrobot and enter qtrobot for the password. Next, enter cd ~/vision-project/docker && ./run.sh run to start the interaction.
Then, you can access the GUI from either 192.168.1.207:8082/low_vision.html or 192.168.1.209:8082/low_vision.html depending on which QT you are using.
Note
Currently, the interaction starts automatically once you access the GUI. After the interaction finishes, it will wait 20 seconds before restarting. Eventually, the interaction will be set to begin only after the GUI screen is clicked/tapped.
Visualizing the interaction¶
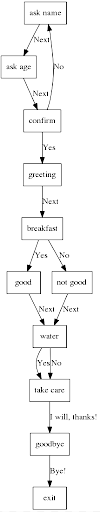
The content of the interaction is contained in a StateCollection object. Use StateCollection.visualize() to view a flowchart of the interaction. By default, the flowchart displays only the name of each node; set the show_content parameter to True to display the entire message.
Here is an example: